Rodent
 The house mouse is one of the most troublesome and economically important rodents in the United States. House mice thrive under a variety of conditions; they are found in and around homes and commercial structures as well as in open fields and agricultural lands. House mice consume and contaminate food meant for humans, pets, livestock, or other animals. In addition, they cause considerable damage to structures and property, and they can transmit pathogens that cause diseases such as salmonellosis, a form of food poisoning.
The house mouse is one of the most troublesome and economically important rodents in the United States. House mice thrive under a variety of conditions; they are found in and around homes and commercial structures as well as in open fields and agricultural lands. House mice consume and contaminate food meant for humans, pets, livestock, or other animals. In addition, they cause considerable damage to structures and property, and they can transmit pathogens that cause diseases such as salmonellosis, a form of food poisoning.
Identification
House mice are small rodents with relatively large ears and small black eyes. They weigh about 1/2 ounce and usually are light brownish to gray in color. An adult is about 5 to 7 inches long, including the 3- to 4-inch tail.
 Droppings, fresh gnaw marks, and tracks indicate areas where mice are active. Mouse nests are made from fine shredded paper or other fibrous material, usually in sheltered locations. House mice have a characteristic musky odor that identifies their presence. Mice are active mostly at night, but they can be seen occasionally during daylight hours.
Droppings, fresh gnaw marks, and tracks indicate areas where mice are active. Mouse nests are made from fine shredded paper or other fibrous material, usually in sheltered locations. House mice have a characteristic musky odor that identifies their presence. Mice are active mostly at night, but they can be seen occasionally during daylight hours.
While the house mouse has not been found to be a carrier of Hantavirus, other mice have. Most notable are the deer mouse and the white-footed mouse, which sometimes invade cabins and outbuildings in California. The house mouse is distinguished from the deer mouse and the white-footed mouse by its overall gray-colored coat. The other two species have a white underside with a distinct line of demarcation between the dark coloration on top and the white underside. In addition, the tail on the house mouse has almost no fur on it, whereas the tails of the deer mouse and the white-footed mouse are moderately to well fur and are light underneath and dark on top.
 Norway rats sometimes called brown or sewer rats, are stocky burrowing rodents that are larger than roof rats. Their burrows are found along building foundations, beneath rubbish or woodpiles, and in moist areas in and around gardens and fields. Nests can be lined with shredded paper, cloth, or other fibrous material. When Norway rats invade buildings, they usually remain in the basement or ground floor. Norway rats live throughout the 48 contiguous United States. While generally found at lower elevations, this species can occur wherever people live.
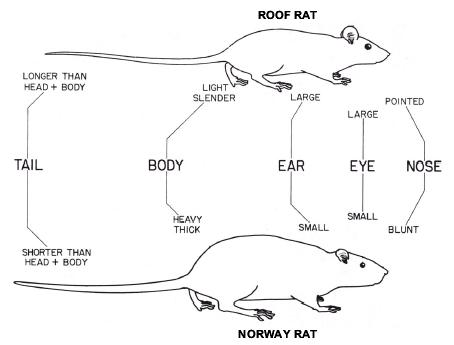
Norway rats sometimes called brown or sewer rats, are stocky burrowing rodents that are larger than roof rats. Their burrows are found along building foundations, beneath rubbish or woodpiles, and in moist areas in and around gardens and fields. Nests can be lined with shredded paper, cloth, or other fibrous material. When Norway rats invade buildings, they usually remain in the basement or ground floor. Norway rats live throughout the 48 contiguous United States. While generally found at lower elevations, this species can occur wherever people live.
Roof rats, sometimes called black rats, are slightly smaller than Norway rats. Unlike Norway rats, their tails are longer than their heads and bodies combined. Roof rats are agile climbers and usually live and nest above ground in shrubs, trees, and dense vegetation such as ivy. In buildings, they are most often found in enclosed or elevated spaces such as attics, walls, false ceilings, and cabinets. The roof rat has a more limited geographical range than the Norway rat, preferring ocean-influenced, warmer climates. In areas where the roof rat occurs, the Norway rat might also be present.
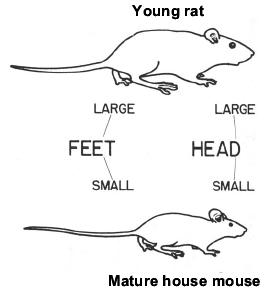
While rats are much larger than the common house mouse, a young rat is occasionally confused with a mouse. In general, very young rats have large heads and feet in proportion to their bodies, whereas those of adult mice are proportionately much smaller. While both rats and mice gnaw on wood, rats leave much larger tooth marks than mice do.

